Tool Mentor: Using RequisitePro to Manage Dependencies
Purpose
This tool mentor describes how to use Rational RequisitePro to manage dependencies by using requirement attributes and traceability.
Related Rational Unified Process activity: Manage Dependencies.
Overview
This Tool Mentor is applicable when running Microsoft Windows 95/NT 4.0.
Requirements are not standalone entities. They are linked to one another, where one requirement might depend on other requirements. They are also linked to other artifacts in the project (such as test cases). Requirements also have different "values", they have different customer priority, different difficulty to implement, different risk associated with them. Requirements dependencies are managed via requirement attributes and traceability links between requirements.
To manage dependencies of requirements:
- Define and associate attributes to requirement types.
- Set attributes values for requirements.
- Define attributes modification security.
- Perform attributes queries.
- Generate requirements attributes reports.
- Establish traceability links between requirements
- Perform traceability queries.
- Perform mixed (attributes and traceability) queries.
- Save queries for reuse.
- Quantify dependency coverage.
- Perform impact analysis.
1. Define and Associate Attributes to Requirement Types

To assign new attributes to requirement types in RequisitePro, follow these steps:
- From the RequisitePro Tool Palette, select Project=>Open, select your RequisitePro project and check the "Exclusive" checkbox. (The project must be opened in exclusive mode to create new attributes).
- Select Project=>Properties. Click on the Attributes tab.
- Select the requirement type for which you wish to define attributes, from the Requirement Type dropdown listbox. The current attributes for that requirement type are listed under the Label title.
- Click on the Add button to add a new attribute to the existing list.
- Enter a label for the new attribute.
- Select an attribute type from the Type dropdown listbox. It is recommended to use the List type for attributes for which you want to constrain user input (thus avoiding the possibility of typos affecting query results).
- For attributes of type List, enter the set of values in the List Values box, separating each value by a carriage return.
- If you want an attribute to possibly be assigned to more than one value, use the List (Multi Value) attribute type.
- If you want changes to an attribute’s value to generate suspect traceability, make sure you turn on the "Change affects suspect" checkbox. This will visually display the traceability link as affected by the attribute value modification. Since not all attributes affect the semantic meaning of the requirement, by default, RequisitePro does not select this checkbox. Carefully choose which attributes can trigger suspect to minimize suspect links management.
- Click OK.
- Click on the "Values per Attribute" radiobutton to set a default attribute value. Note that changing the default value of an attribute after requirements have been created only affects requirements created after that point. Therefore, it is recommended to select a default attribute value at creation of that attribute so that each new requirement has assigned default attribute values automatically. Select the default value from the list, and click the Default button. Click OK.
2. Set Attributes Values for Requirements 
Once attributes have been defined for each requirement type, requirements of that type will automatically inherit these attributes and its default values. To assign attribute values to a requirement, follow these steps:
- Select "Switch to the Views workplace" from the RequisitePro’s Tool Palette.
- Create a new attribute matrix by clicking on the "Create a new view" icon, selecting "Attribute Matrix", and the specific requirement type.
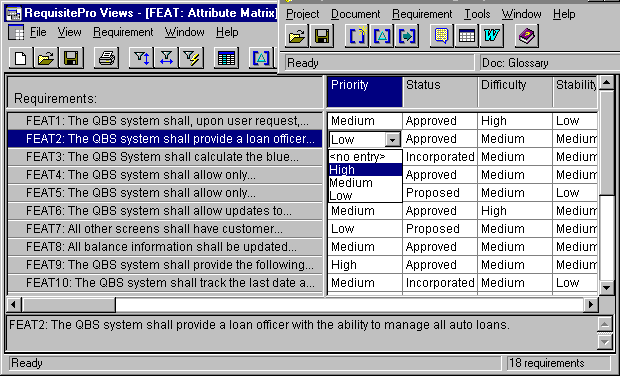
- Click at the intersection of the requirement row and the attribute column. This makes the intersection cell editable. Enter the attribute value. If the attribute is of type List, a dropdown list of valid values is displayed. If the attribute is not of type List, simply enter the attribute value directly in the cell. The value of the attribute is automatically entered in the RequisitePro repository when the focus moves to another cell.
- To set an attribute value to all requirements in a view, use the Requirement=>Attribute Fill option from the Views menu.
- To set the same attribute value to a subset of requirements in a view, select the requirements (using the SHIFT and/or CTRL keys), click on the attribute column of the attribute to modify, then select Requirements=>Set Attribute from the Views menu. Choose an attribute value. All selected requirements are assigned the selected attribute value. Click OK.
- For attributes of type List (Multi Value), you will be presented with a dropdown listbox to select multiple values. Select values one at a time.
3. Define Attributes Modification Security 
The last user to modify an attribute value defines the attribute value stored in the repository. By default RequisitePro allows all users to modify all attribute values. You can modify security settings to restrict attribute value settings to only a subset of users. Rules on who can modify which attribute and who can set an attribute to which subset of values can be defined. To define such rules, RequisitePro provides security from the document level all the way to a specific attribute value level. By default, project security is turned off.
- To turn project security on, select Project->Security from the RequisitePro’s Tool Palette.
- Turn on the Enable security for this project checkbox.
- Create new groups as needed by clicking on the Add button in the Groups groupbox..
- For each selected group, click on the Add button in the Users groupbox to create users and assign each a username, password and optionally an email address.
- To assign group privileges, select a group on the left and click Edit.
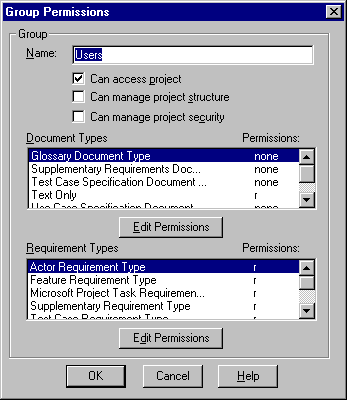
- To set attribute security, select a requirement type in the Requirement Types groupbox and click on the Edit Permissions button below.
- Turn Update on.
- Select the attribute to which you want to set security, and click Edit Permissions.
- For attributes of type List, the list of valid values will be displayed. Select each value and click on Edit Permissions.
- Turn Update on or off to allow or disallow write access to that attribute value for all users of the selected group.
- Click OK until all dialogs are dismissed.
4. Perform Attributes Queries 
Once attribute values have been set, it is helpful to view requirements of specific attribute values. For instance, it might be interesting to only look at requirements whose priority is high and difficulty is low. To query requirements based on attributes, follow these steps:
- Click "Switch to the Views workplace" on the RequisitePro’s Tool Palette.
- Click "Switch to the Views workplace" on the RequisitePro’s Tool Palette.
- Create a new attribute matrix by clicking on the "Create a new view" icon, selecting "Attribute Matrix", and the specific requirement type.
- Click on the "Filter and Sort Row" icon or select View=>Query Row Requirements from the Views menubar. This brings up a point-and-click interface to select filter criteria.
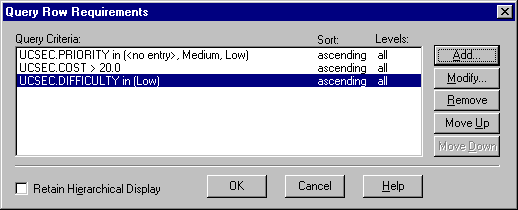
- Select one attribute and click OK. Depending on the type of the selected attribute, different dialogs will come up to set the attribute value criteria. On any of these dialogs, you can also determine the Sort Order, and restrict the search to a specific hierarchical level if you use hierarchical requirements.
- Define or select the attribute value(s) criteria and click OK.
- At this point, you can click Add to create compound queries, Modify to change an existing query, or Remove to remove a query. In compound queries, all listed criteria are AND-ed together.
- Notice on that dialog the "Retain Hierarchy Display" checkbox. This checkbox allows options for the displayed results. The query engine will compare all requirements, whether parent or child, against the query criteria defined by the user. If a child requirement meets the criteria but its parent does not, you have the option to display only the child as a result, or display the child as well as its parent (to provide the child context).
- Refer to the Traceability Concept for sample useful queries to perform.
- Note that both the row requirements and the column requirements can be queried independently.
5. Generate Requirements Attributes Report 
The Artifact: Requirements Attributes provides a summary of the status of all requirements. To create this artifact in RequisitePro, follow these steps:
- Select "Switch to the Views workplace" from the RequisitePro’s Tool Palette.
- Create a new Attribute Matrix by clicking on the "Create a new view" icon, selecting the requirement type you want to report on, and selecting "Attribute Matrix". An attribute matrix is displayed.
- You can choose which specific attributes you want to view:
- Click on the "Filter and Sort Columns" icon on the Views toolbar.
- Select the specific attributes you want to view, and select the Display Order.
- Click OK. This will display your customized attribute matrix.
- You can then save this customization by saving the view (which saves the parameters of this view, not the data).
- Select File=>Save View As. Enter a name for this view. Readers of Artifact: Requirements Attributes are everyone in the development organization, so select "Project-wide". RequisitePro also allows you to save personal views that are only viewable by the view creator. Note that the views are saved as part of the RequisitePro project, so all Requirement Attributes artifacts will be put under configuration management control when the RequisitePro project is put under CM control.
6. Establish Traceability Links Between Requirements 
As high level requirements, such as product features, are decomposed into more detailed requirements such as software specifications, traceability links will ensure that the more detailed requirements are related to the original higher level requirement. This allows for impact analysis when requirements change, using RequisitePro’s suspect link feature. Traceability links also allow maintenance of dependency relationships between two requirements at the same level.
You should determine your project’s requirements structure and what traceability links are required for your project and your requirements. Once you have done this, do the following in RequisitePro to create the traceability links.
In RequisitePro, traceability can be set in various ways:
- Set or Remove traceability from a traceability matrix
This is probably the easiest way to set/remove traceability links. Follow these steps:
- Create a Traceability Matrix by selecting "Show the Views workplace" from the RequisitePro Tool Palette and clicking on the "Create a new view" icon.
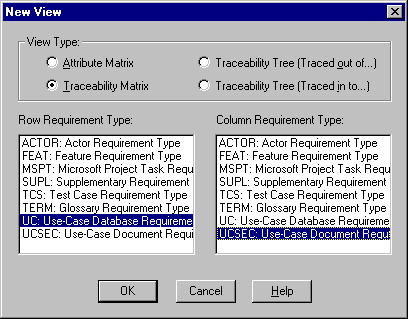
- Select the two requirement types to create a NxM matrix. You may choose the same requirement type twice to establish dependency links between several requirements of the same type.
- Once the matrix is displayed, right-click on the intersection between the two requirements to link and select TraceTo. (Note: the difference between TraceTo and TraceFrom is purely subjective. The one rule to follow is to only use one of them within a RequisitePro project, either TraceTo, or TraceFrom. A good rule of thumb is to make the arrow point from a requirement to what it is dependent upon). To remove a link, select Remove Trace.
You will notice an arrow icon displayed at the intersection. This is a visual clue that there is a traceability link between the two selected requirements.
- Set or Remove traceability from the Requirement dialog
Whether in the Word workplace or in the Views workplace, you can invoke the Requirement dialog and set/remove traceability in the Traceability tab.
- To invoke the Requirement dialog from the Word workplace, position your cursor in the middle of the requirement text and select Requirement=>Properties. Click on the Traceability tab.
- To invoke the Requirement dialog from the Views work, select the requirement row in a view, right click and select Properties. Click on the Traceability tab. Add or Remove traceability links.
- Set or Remove traceability from a traceability tree
- Select "Switch to the Views workplace" from the RequisitePro’s Tool Palette.
- Create a new Traceability Matrix by clicking on the "Create a new view" icon, selecting the requirement type you want to report on, and selecting "Traceability Matrix". A traceability matrix is displayed. You can also create a traceability tree.
- Click on the "Filter and Sort Row" icon or select View=>Query Row Requirements or View=>Query Column Requirements from the Views menubar. This brings up a point-and-click interface to select filter criteria.
- Depending whether you used TraceTo or TraceFrom, select one of the two traceability attributes, Traced-to or Traced-from.
- Select the requirement type displayed in the active traceability matrix. Select either Not Traced to query on missing links or Suspect Only to query on affected links. Click OK.
- At this point, you can click Add to create compound queries, Modify to change an existing query, or Remove to remove a query. In compound queries, all listed criteria are AND-ed together.
- Notice on that dialog the "Retain Hierarchy Display" checkbox. This checkbox allows options for the displayed results of hierarchical requirements. The query engine will compare all requirements, whether parent or child, against the query criteria defined by the user. If a child requirement meets the criteria but its parent does not, you have the option to display only the child as a result, or display the child as well as its parent (to provide the child context).
- Refer to the Traceability Concept for sample useful queries to perform.
- Note that both the row requirements and the column requirements can be independently queried.
- Select "Switch to the Views workplace" from the RequisitePro’s Tool Palette.
- Create a new Traceability Matrix by clicking on the "Create a new view" icon, selecting the requirement type for software specifications, selecting the requirement type for test cases and select "Traceability Matrix". A traceability matrix is displayed.
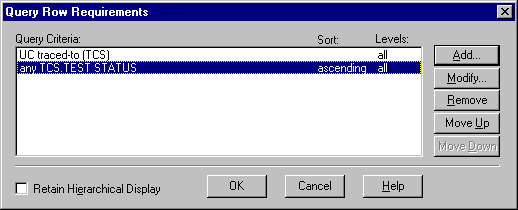
- Click on the "Filter and Sort Row" icon or select View=>Query Row Requirements from the Views menubar. This brings up a point-and-click interface to select parameters for the software specification requirements.
- Select Traced-to to query on test cases traced to software specifications. Click OK.
- The Query Requirements dialog is displayed. Deselect all selection and select the Test Cases Requirement Type. Click OK.
- The Query Row Requirements dialog is displayed.
- Click Add to add a query about the passing status of test cases.
- Select the Test Case Requirement Type, and select the Test Status attribute. Click OK.
- A dialog comes up to select Test Status attribute values.
- Select the Failed as Test Status value to query. Click OK. The compound query is displayed.
- Click OK to dismiss the dialog. RequisitePro displays the results of this compound query in a matrix. All software specifications whose test cases failed are displayed.
- Refer to the Traceability Concept for sample useful queries to perform.
- To save a view, from the Views menubar select File=>Save View. You may choose to save the view as Personal or as Project Wide. Project Wide saved views are accessible by all users of the project, regardless of security settings. Personal views are only accessible to the user who created that view. Provide a meaningful name to your view (for instance: "PRxSR suspects"), and click OK.
- To restore a view, from the Views menubar select File=>Open View. Select the saved view name. This will perform the query attached to that saved view on the current set of requirements and display the results.
- Create a view of any type (attribute matrix, traceability matrix or traceability tree).
- Invoke the query engine by clicking on one of the "Filter and Sort" icons.
- Select the attribute labeled Traced-to (or Traced-from depending on which one your project uses).
- Select the requirement type(s) you are interested in. You might leave the default Select All for a start. Notice on the dialog the option of "Not Traced". By selecting this option, you can get a view of the high level requirements not traced to any other lower level requirements.
- Create a view of any type (attribute matrix, traceability matrix or traceability tree).
- Invoke the query engine by clicking on one of the "Filter and Sort" icons.
- Select the attribute labeled Traced-to (or Traced-from depending on which one your project uses).
- Select the requirement type(s) you are interested in. You might leave the default Select All for a start. Notice on the dialog the option of "Not Traced" and "Suspect only". By selecting both of these options, you can get a view of all traceability links that have been affected by some requirement changes. From there, you would investigate each requirement involved in a suspect traceability link by doing the following:
- Select the requirement to investigate, and select Properties (right clicking in a View, or click on the Modify icon on the Tool Palette).
- Click on the Revision tab, then click on the History button. This dialog details all changes that occur with this requirement, including who made the change, when, why and a definition of the change itself.
- Position the cursor on the suspect link icon in a traceability matrix or tree, right click and select Clear Suspect. This will erase the red slash on the traceability icon.
- If the modified requirement is traced to several requirements of the same type, from a traceability matrix you can use the Requirement=>Traceability Fill menu item from the Views menubar to Clear Suspect multiple suspect links at once.
From a traceability tree, you can right click on a requirement and select TraceTo or Properties from the popup menu. A Remove Trace option is also provided.
7. Perform Traceability Queries 
Once traceability relationships have been set, it is helpful to query these links. For instance, it might be interesting to measure how many product features have not yet been traced to detailed software specifications, or how many software specifications do not have attached test cases. See Concept:Traceability for examples of pertinent queries. To query on traceability, follow these steps:
8. Perform Mixed Queries 
Some of the most powerful queries actually involve both traceability and attributes. For instance, an important query might be:
Show me all software specifications that are traced to test cases, but whose test cases failed.
To perform such a query:
9. Save Queries for Reuse 
You might find yourself always doing the same queries in a project. RequisitePro allows users to save queries for reuse. A view contains the results of a query. Saving a view will save the query criteria. When the view is restored, the query criteria is applied to all current requirements in the project.
10. Quantity Dependency Coverage 
Setting traceability links allows users to insure that all high level requirements are being traced down to lower level requirements, such as software requirements and test requirements. With a large number of requirements, it can be cumbersome to measure how many dependencies have been set and which ones are missing. RequisitePro’s query engine allows queries on attributes as well as on traceability relationships. For instance, you might want to know how many product features have not been traced to any software requirements. This would indicate which product features still need to be decomposed in lower level requirements for engineers to be able to include these features in the next release. To perform such a query, follow these steps:
11. Perform Impact Analysis 
Setting traceability links between requirements also allows users to monitor impact of requirement changes. As requirements change (either the text of the requirement changes or an attribute set to Change affects Suspect changes), traceability links are marked as suspects links, indicated visually by a red slash over the traceability icon. A suspect link is your indication that something has changed in one of the two requirements linked by traceability, and that you should investigate the possible impact of that change. The query engine can be used to report on suspect links. Follow these steps:
At this point, a user would make a decision whether that requirement change may have an impact on requirements traced to or from the change requirement. If the change has no measurable impact, then the suspect link should be cleared by doing the following:
![]()