Concepts: Traceability
The purpose of establishing traceability is to help:
- Verify that all requirements of the system are fulfilled by the implementation.
- Verify that the application does only what it was intended to do.
- Manage change.
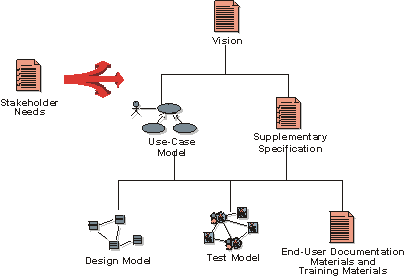
The traceability hierarchy.
Traceability helps you follow how stakeholder needs are translated into a set of features in the Vision document, which in turn is detailed into use cases and Supplementary Specifications. You then need to follow how these detailed specifications are translated into a design, how it is tested, and how it is documented for the user.
Your traceabilities should be set up so that they help you answer the following sample set of queries:
- Show me user needs that are not linked to product features.
- Show me the status of tests on all use cases in iteration #n.
- Show me all supplementary requirements linked to tests whose status is untested.
- Show me the results of all tests that failed, in order of criticality.
- Show me the features scheduled for this release, which user needs they satisfy, and their status.
Example:
For a Recycling Machine system, the Vision document specifies the following feature:
PR10:The recycling machine will allow the addition of new bottle types.>
This feature is traced to a use case "Add New Bottle Type":
The use case Add New Bottle Type allows the Operator to teach the Recycling Machine to recognize new kinds of bottles.
This traceability helps us verify that all features have been taken care of in use cases and supplementary specifications.
![]()