Guidelines: Design Model
|
The design model is an object model describing the realization of use cases, and serves as an abstraction of the implementation model and its source code. |
Topics
Definition 
The design model is adapted to model the real implementation environment, and serves as an abstraction of the source code. It is a "blueprint" of how the source code is structured and written.
The design model is a hierarchy of packages (design subsystems and design packages), with "leaves" that are classes or use-case realizations.
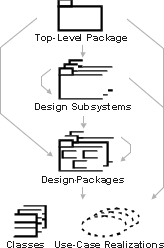
The design model hierarchy. Arrows show possible ownership.
Classes represent abstractions of classes in the system's implementation. They define the objects, which in turn are abstractions of the objects in the system's implementation. The use cases are realized by the objects, and this is represented by use-case realizations. Each use-case realization in the design model has a trace dependency to a use case in the use-case model.
Mapping to the Implementation Model 
You should decide before the design starts how classes in the design model should relate to implementation classes; this should be described in the Design Guidelines specific to the project.
The design model can be more or less close to the implementation model, depending on how you map its classes, packages and subsystems to components, packages and subsystems in the implementation model. During implementation, you will often address small tactical issues related to the implementation environment that shouldn't have impact on the design model. For example, classes and subsystems can be added during implementation to handle parallel development, or to adjust import dependencies. For more information, refer to Activity: Structure the Implementation Model and Concepts: Mapping from Design to Code.
There should be a consistent mapping from the design model to the implementation model. The Artifact: Design Guidelines should define this mapping, and a consistent level of abstraction should be applied across the design model.
What Is a Good Design Model?
A good design model has the following characteristics:
- It satisfies the system requirements.
- It is resistant to changes in the implementation environment.
- It is easy to maintain in relation to other possible object models and to system implementation.
- It is clear how to implement.
- It does not include information that is best documented in program code.
- It is easily adapted to changes in requirements.
![]()