Guidelines: Actor-Generalization
Actor-Generalization |
An actor-generalization from an actor type (descendant) to another actor type (ancestor) indicates that the descendant inherits the role the ancestor can play in a use case. |
Topics
Explanation 
Several actors can play the same role in a particular use case. Thus, a Teller and an Accountant, both of whom check the balance of an account, are seen as the same external entity by the use case that does the checking. The shared role is modeled as an actor, Balance Supervisor, inherited by the two original actors. This relationship is shown with actor-generalizations.
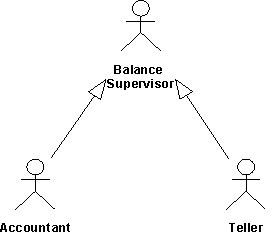
The actors Teller and Accountant inherit all the properties of a Balance Supervisor. Thus, both these actors can act as Balance Supervisors.
Use 
A user can play several roles in relation to the system, which means that the user may, in fact, correspond to several actors. To make the model clearer, you can represent the user by one actor who inherits several actors. Each inherited actor represents one of the user's roles relative to the system.
![]()